Final Report/Thesis 2015
Executive Summary
Introduction
Motivation
Previous Studies/Related Work
Aims and Objectives
Significance
Technical Background
P-Value Theorem Explanation
Chi-Squared Test Explanation
Universal Declaration of Human Rights Explanation
Project Gutenberg Explanation
N-Gram Model Explanation
One-Time Pad Explanation
Knowledge Gaps and Technical Challenges
Method - Specific Tasks
Task 1: Statistical Frequency Analysis of Letters
Aim
Method
Results
Evaluation and Justification
Task 2: N-Gram Search
Aim
Method
Results
Evaluation and Justification
Task 3: Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam as a One-Time Pad
Aim
Method
Results
Evaluation and Justification
Task 4: Statistical Frequency of Letters Reanalysis
Aim
Method
Results
Evaluation and Justification
Project Management - Planning and Feasibility
Work Breakdown/Deliverables
Timeline
The timeline for this project was created in the form of a Gantt Chart. The proposed Gantt Chart can be seen in Figure 3.
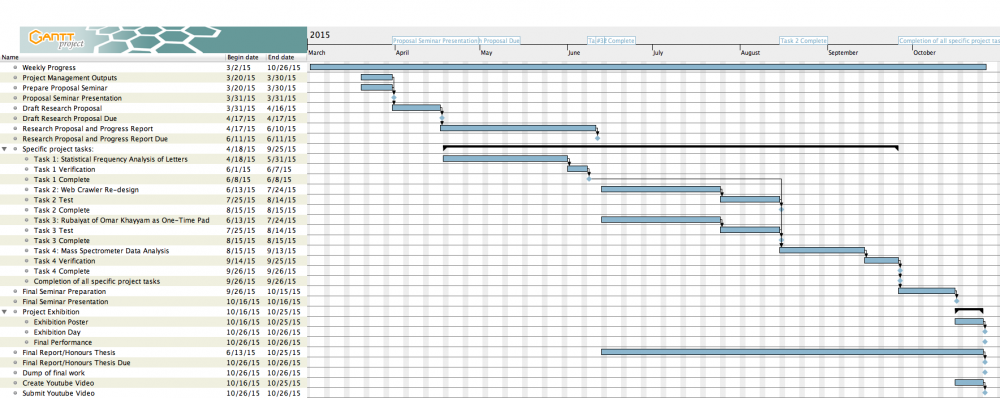
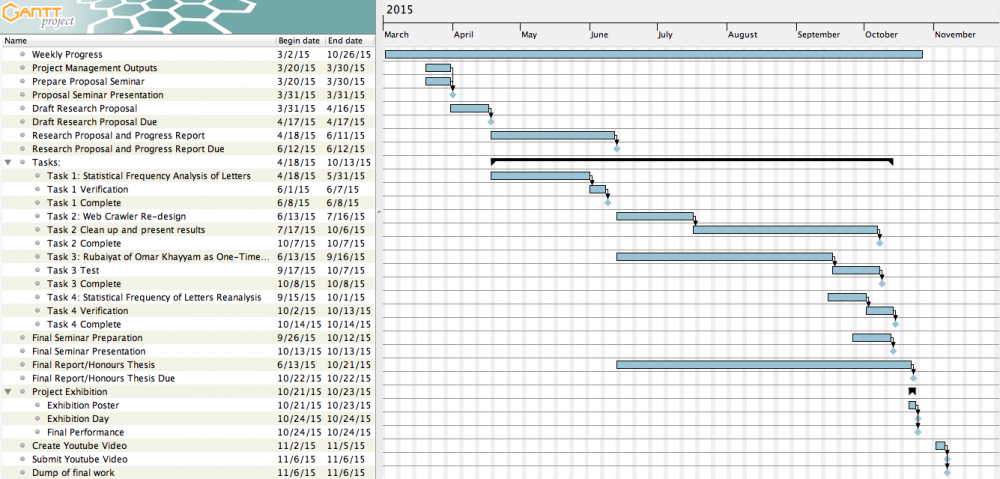
The final Gantt Chart after all revisions and updates can be seen in Figure X.
Task Allocation
Management Strategy
Budget
Risk Analysis
Conclusions
Future Work
References
Glossary and Symbols
- ASIO: Australian Security Intelligence Organisation
- ASIS: Australian Secret Intelligence Service
- ASD: Australian Signals Directorate
- P-value theorem: The p-value is the calculated probability that gives researchers a measure of the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis [1].
- Chi-Squared Test:
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights:
- Project Gutenberg:
- N-gram model: The N-gram model is a sequence of n items from a given sequence of phonemes, syllables, letters, words or base pairs [2].
- One-time pad: The one-time pad is a decoder technology which cannot be cracked if the correct key is used [3].
- Initialism: A group of letters formed using the initial letters of a group of words or a phrase [4].
- Ciphertext: The encoded format of a message [5].
- Plaintext: The information of an original message, which is desired to be deciphered from the ciphertext </ref>.
http://www.maths.uq.edu.au/~pa/SCIE1000/gma.pdf</ref>.
- Key: What is needed to convert the ciphertext into the plaintext using the one-time pad </ref>.
- ↑ B. David et al., “P Value and the Theory of Hypothesis Testing: An Explanation for New Researchers,” Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®, Vol.468 (3), pp.885-892 2010. [25] G G. L et al., “What is the Value of a p Value?,” The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, Vol.87(5), pp.1337-1343 2009. [26] No Author.p-value [online]. Available: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P-value#cite_note-nature506-1
- ↑ A. Z Broder et al., “Syntactic clustering of the web”. Computer Networks and ISDN Systems 29 (8), pp.1157–1166. [28] No Author. Video Lectures [online]. Available: https://class.coursera.org/nlp/lecture/17
- ↑ S.M. Bellovin. (2011, July 12). Frank Miller: Inventor of the One-Time Pad [online]. Available: http://www.tandfonline.com.proxy.library.adelaide.edu.au/doi/full/10.1080/01611194.2011.583711#abstract
- ↑ No Author. Initialism [online]. Available: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/initialism
- ↑ No Author (2011). Topic 1: Cryptography [online]. Available: http://www.maths.uq.edu.au/~pa/SCIE1000/gma.pdf